what is the difference between 134 and 134a
Understanding the Difference Between 134 and 134a A Comprehensive Overview
In the realm of refrigeration and air conditioning, refrigerants play a critical role in facilitating heat transfer. Among the various refrigerants available, two of the most commonly discussed are R-134 and R-134a. Although their names are similar, their characteristics, applications, and environmental impacts differ significantly. This article aims to clarify these differences to better understand their uses in modern cooling systems.
Firstly, it’s essential to identify that R-134 and R-134a refer to different substances, although both belong to the hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) family. R-134, more formally known as R-134, is not typically used in modern applications, whereas R-134a is the widely recognized refrigerant utilized in automotive air conditioning systems, refrigerators, and commercial cooling applications.
Chemical Composition and Properties
R-134a, or 1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane, has a molecular structure that features four fluorine atoms and two carbon atoms. This unique configuration gives it specific thermodynamic properties that make it suitable for various refrigeration needs. It operates efficiently at lower temperatures and is non-flammable, which makes it safe for use in household appliances and automotive systems.
On the other hand, R-134 does not have the same standing in the industry. It usually refers to a product that is either outdated or incorrect. The refrigerant commonly accepted and used today is R-134a, which adheres to contemporary environmental standards.
what is the difference between 134 and 134a
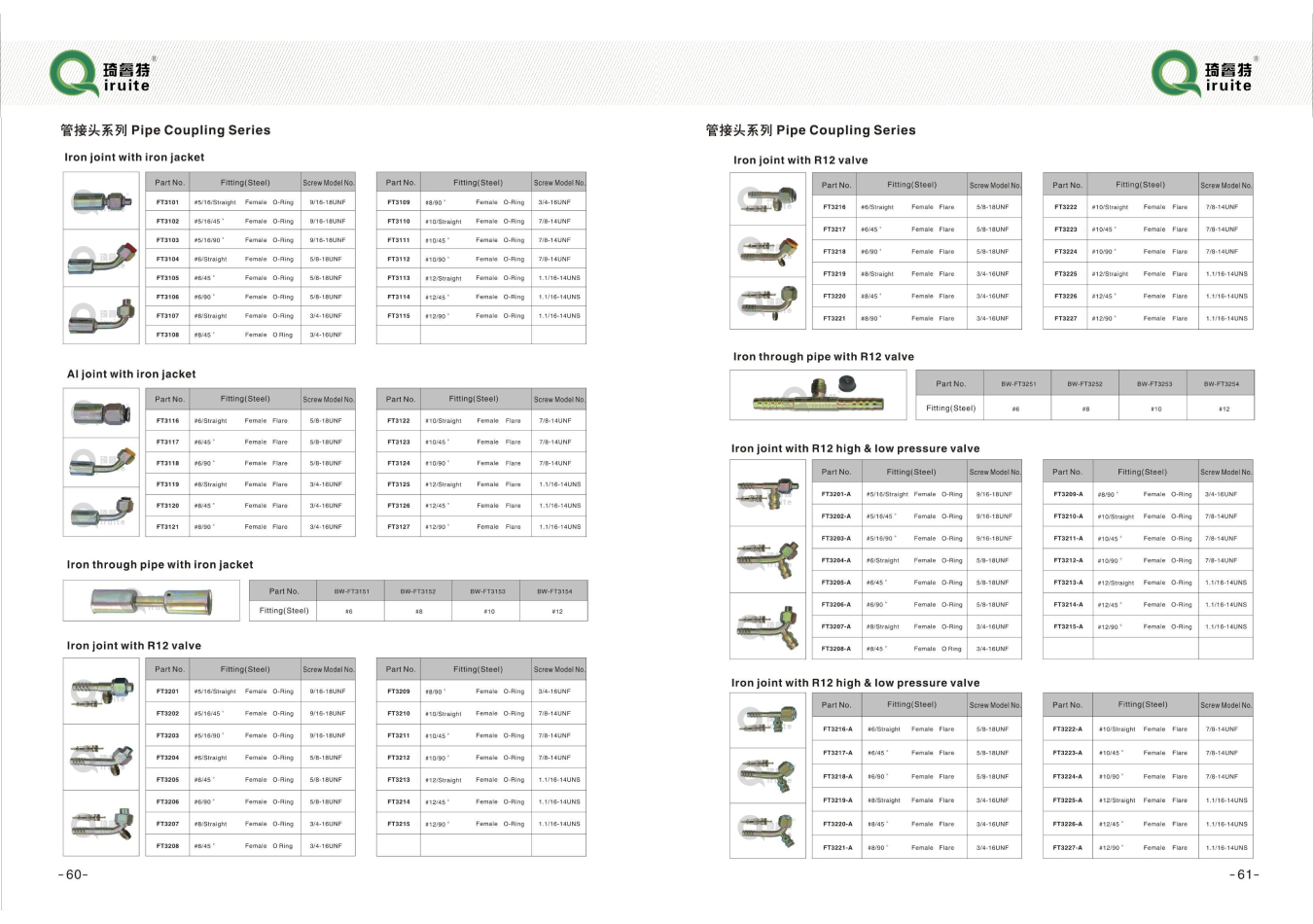
Environmental Impact
When discussing refrigerants, one of the most critical factors to consider is their impact on the environment. R-134a has a Global Warming Potential (GWP) of about 1,430, which indicates its capacity to contribute to greenhouse gas warming effects compared to carbon dioxide over a 100-year period. While R-134a was considered a more environmentally friendly option compared to older refrigerants like R-12, it is still subject to scrutiny given the push for more eco-friendly alternatives.
In recent years, there has been an increasing shift towards low-GWP alternatives, such as hydrofluoroolefins (HFOs), which show promise in reducing the overall environmental impact of refrigerants. Understanding the differences between R-134 and R-134a and the transition to greener options is crucial for industry professionals and consumers alike.
Applications
R-134a is the preferred choice in applications ranging from automotive cooling systems to commercial refrigeration. Its efficiency and safety features make it an ideal refrigerant for modern HVAC systems. There is little to no mention of R-134 in current specifications as it does not meet the modern requirements for effective cooling performance.
In conclusion, while R-134 and R-134a may sound similar, their differences are significant, especially in their chemical properties, environmental impact, and practical applications. Understanding these distinctions is vital for anyone involved in refrigeration and air conditioning, as the industry moves toward more sustainable and environmentally responsible refrigerant options.
-
Ultimate Spiral Protection for Hoses & CablesNewsJun.26,2025
-
The Ultimate Quick-Connect Solutions for Every NeedNewsJun.26,2025
-
SAE J1401 Brake Hose: Reliable Choice for Safe BrakingNewsJun.26,2025
-
Reliable J2064 A/C Hoses for Real-World Cooling NeedsNewsJun.26,2025
-
Heavy-Duty Sewer Jetting Hoses Built to LastNewsJun.26,2025
-
Fix Power Steering Tube Leaks Fast – Durable & Affordable SolutionNewsJun.26,2025

