3 4 pipe coupling dimensions
Understanding 3% and 4% Pipe Coupling Dimensions
Pipe couplings are essential components in fluid transport systems, serving as connectors for different sections of piping. They allow for the easy assembly or disassembly of pipe systems, making maintenance and adjustments straightforward. Among the various types of couplings available, 3% and 4% couplings have particular characteristics and dimensions that make them preferable in specific applications. This article explores the dimensions and uses of 3% and 4% pipe couplings, as well as their importance in industrial settings.
What Are Pipe Couplings?
Pipe couplings are fittings that join two lengths of pipe together. They can be used in various materials, including metal, plastic, and composite materials. Typically, couplings come in several types, including threaded, slip, and welded, each serving a different purpose depending on the application. The choice between 3% and 4% couplings often depends on the dimensions of the pipes being connected and the specific requirements of the installation.
Dimensions and Specifications
The dimensions of 3% and 4% pipe couplings refer to the nominal size and pressure ratings of the pipes they are designed to accommodate
. The term 3% typically signifies a coupling that fits pipe diameters around 3 inches, while 4% refers to a 4-inch pipe diameter.For a 3% coupling, the standard dimensions often include an outer diameter of approximately 3.5 inches, with a typical wall thickness that can vary depending on the material and pressure rating. The internal diameter generally considers the pipe wall thickness, making it essential for determining flow capacity and compatibility with the pipes being used.
On the other hand, a 4% coupling usually has an outer diameter of about 4.5 inches. Like the 3% coupling, the wall thickness can change based on the specific requirements and pressure ratings and is crucial for ensuring the integrity of the connection under operating conditions.
3 4 pipe coupling dimensions
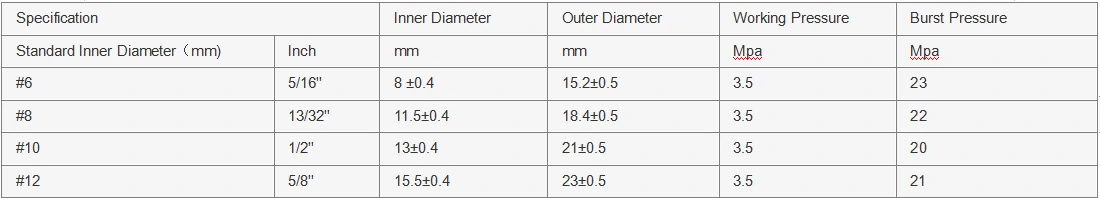
Applications of 3% and 4% Couplings
3% and 4% couplings are widely utilized across various industries, including oil and gas, water treatment, construction, and HVAC systems. The choice of coupling size is primarily dictated by the type of pipes (e.g., PVC, steel, or copper) and the specific fluid being transported.
In oil and gas, for instance, a 3% coupling might be used for smaller pipeline systems, facilitating effective flow management in situations where space is limited. Meanwhile, a 4% coupling can be critical in larger industrial applications where increased flow rates are required.
Importance of Proper Selection
Choosing the wrong coupling size can lead to significant issues, including leaks, increased maintenance costs, and even potential system failures. It is crucial to consider the pressure ratings and the materials being used in conjunction with the coupling dimensions to ensure an optimal fit. Additionally, adhering to industry standards and guidelines can enhance the reliability and safety of the entire piping system.
Conclusion
In summary, the correct understanding and selection of 3% and 4% pipe coupling dimensions play a pivotal role in the efficiency and safety of piping systems across various applications. By considering factors such as material compatibility, flow requirements, and pressure ratings, engineers and technicians can select the most appropriate couplings that will ensure a robust and reliable connection. Maintaining the integrity of these connections is critical to successful fluid transport operations in any industrial setting.
-
Ultimate Spiral Protection for Hoses & CablesNewsJun.26,2025
-
The Ultimate Quick-Connect Solutions for Every NeedNewsJun.26,2025
-
SAE J1401 Brake Hose: Reliable Choice for Safe BrakingNewsJun.26,2025
-
Reliable J2064 A/C Hoses for Real-World Cooling NeedsNewsJun.26,2025
-
Heavy-Duty Sewer Jetting Hoses Built to LastNewsJun.26,2025
-
Fix Power Steering Tube Leaks Fast – Durable & Affordable SolutionNewsJun.26,2025

