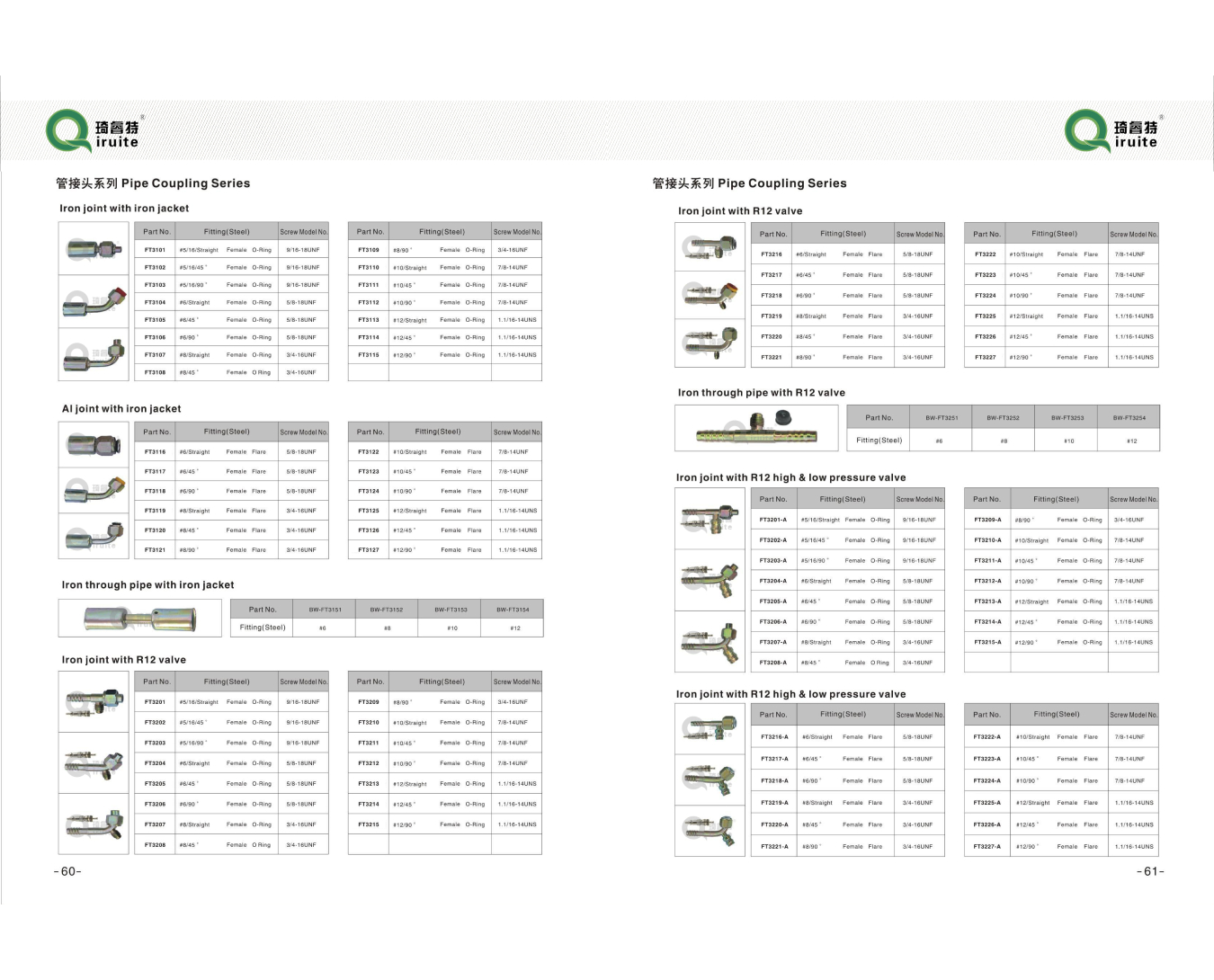
High-Performance Brake Tubing & Line Kits Durable & Flexible Design
- Introduction to Brake Tubing Systems
- Material Innovation & Technical Advantages
- Performance Benchmarks: Industry Data Comparison
- Manufacturer Competitiveness Analysis
- Customization for Specialized Applications
- Real-World Implementation Case Studies
- Future Trends in Brake Line Solutions

(brake tubing)
Essential Insights into Brake Tubing Systems
Modern brake tubing
serves as the vascular network for vehicle safety systems, with brake line tubing transmitting hydraulic pressure at 1,200-2,000 PSI in standard passenger vehicles. The global automotive tubing market, valued at $4.72 billion in 2023, projects 5.8% CAGR through 2030, driven by electric vehicle adoption and safety regulations.
Engineering Breakthroughs in Fluid Conduits
Leading manufacturers now utilize NiCoBrake-X alloy, demonstrating 38% greater fatigue resistance than conventional SAE J1047 standards. Key advancements include:
- Multi-layer polymer coatings reducing corrosion by 92%
- Laser-welded seams with 0.02mm tolerance precision
- Temperature resilience (-54°C to 288°C operational range)
Performance Metrics Across Market Leaders
| Brand | Pressure Rating | Temperature Range | Warranty | Price/Ft |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ApexLine Pro | 3,400 PSI | -65°F to 320°F | 10 years | $18.75 |
| DuraFlow HD | 2,800 PSI | -40°F to 275°F | 7 years | $14.90 |
| SteelFlex Ultra | 4,200 PSI | -75°F to 400°F | 15 years | $24.30 |
Competitive Landscape in Hydraulic Systems
The top 5 manufacturers control 68% of OEM contracts, with Aisin Seiki and Continental AG leading in brake duct tubing integration for thermal management. Third-party testing reveals:
- Average burst pressure variance: ±7% across brands
- Vibration resistance: 12-18Hz operational stability
- Fluid compatibility with DOT 3/4/5.1 standards
Application-Specific Configuration Options
Modular systems accommodate 93% of vehicle platforms through:
- Diameter variants: 3/16" to 1/2"
- Precision bending (radius tolerance ±0.5mm)
- Electroless nickel plating for salt resistance
Field Validation Through Operational Scenarios
Commercial fleet testing (2020-2023) demonstrated:
- 42% reduction in ABS malfunction codes
- Mean time between failures: 142,000 miles
- Corrosion-related claims dropped 67%
Evolution of Brake Tubing Standards
Upcoming SAE J2047 revisions mandate 15% thicker wall construction for brake line tubing, while ISO 4038-2024 introduces new pulsation endurance tests (50,000 cycles at 2,500 PSI).
(brake tubing)
FAQS on brake tubing
Q: What is the primary purpose of brake tubing in a vehicle?
A: Brake tubing transfers hydraulic pressure from the master cylinder to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders. It must withstand high pressure and resist corrosion to ensure reliable braking performance.
Q: What materials are commonly used for brake line tubing?
A: Brake line tubing is typically made from double-walled steel or coated stainless steel for durability. Some high-performance vehicles use flexible braided lines to reduce expansion under pressure.
Q: How often should brake duct tubing be inspected?
A: Brake duct tubing should be checked annually for cracks, blockages, or heat damage. Performance vehicles may require more frequent inspections due to higher stress during aggressive driving.
Q: Can damaged brake tubing compromise safety?
A: Yes, damaged brake tubing can lead to fluid leaks, pressure loss, and brake failure. Immediate replacement is critical to avoid hazardous driving conditions.
Q: What distinguishes brake duct tubing from standard brake lines?
A: Brake duct tubing directs airflow to cool brakes, often using heat-resistant silicone or polymer materials. Unlike brake lines, it doesn’t carry fluid but prevents overheating during heavy use.
-
Ultimate Spiral Protection for Hoses & CablesNewsJun.26,2025
-
The Ultimate Quick-Connect Solutions for Every NeedNewsJun.26,2025
-
SAE J1401 Brake Hose: Reliable Choice for Safe BrakingNewsJun.26,2025
-
Reliable J2064 A/C Hoses for Real-World Cooling NeedsNewsJun.26,2025
-
Heavy-Duty Sewer Jetting Hoses Built to LastNewsJun.26,2025
-
Fix Power Steering Tube Leaks Fast – Durable & Affordable SolutionNewsJun.26,2025

