High-Quality 3% Pipe Coupling Solutions for Efficient Plumbing and Piping Systems
Understanding 3% Pipe Coupling A Key Component in Fluid Transport Systems
In the world of industrial manufacturing and plumbing, the details of pipe connections can often be overlooked. However, one small but crucial component that plays a significant role in the integrity and efficiency of these systems is the pipe coupling. Among various types of couplings, the 3% pipe coupling has gained prominence due to its specific applications and benefits.
A pipe coupling is essentially a mechanical device that connects two pipes. It serves various functions such as aligning, sealing, and supporting the flow of fluids or gases through the pipeline. The designation of “3%” refers to the percentage of certain material properties, often indicating tolerance levels or a specific design characteristic that influences the performance of the coupling, particularly in high-pressure applications.
Understanding 3% Pipe Coupling A Key Component in Fluid Transport Systems
Materials used in the construction of 3% pipe couplings are typically high-quality metals or polymers, selected based on the nature of the fluid being transported. For instance, in chemical processing, resistant materials that can withstand corrosive elements are essential. The choice of material also directly influences the coupling’s durability, longevity, and suitability for specific applications.
3 pipe coupling
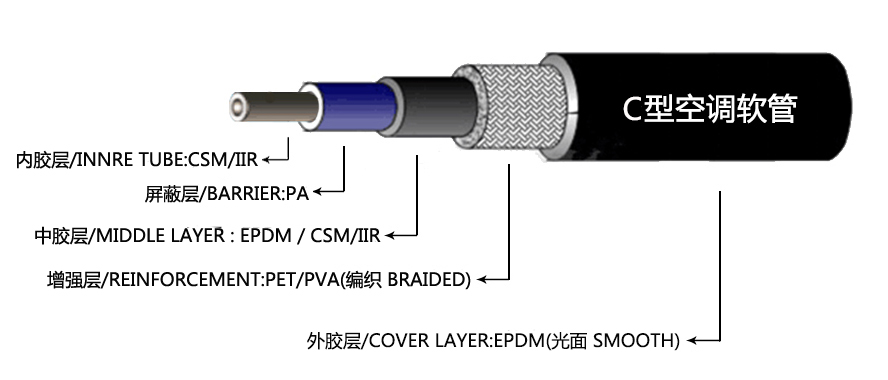
The installation of a 3% pipe coupling is another area where attention to detail is paramount. A properly installed coupling reduces the risk of leaks and ensures that the flow is optimized within the pipeline network. Various methods of installation exist, including threaded, flanged, and welded couplings, each providing different advantages depending on the context. For instance, welded couplings are often preferred in high-pressure systems due to their robustness, whereas threaded couplings might be more suitable for applications requiring ease of disassembly.
It's also important to note that regular maintenance and inspection of pipe couplings are essential for any fluid transport system. Over time, factors such as abrasion, corrosion, and thermal expansion can affect the performance of the coupling. By proactively monitoring the condition of these critical components, operators can prevent premature failures and maintain the efficiency of the overall system.
Moreover, as industries evolve and standards for safety and efficiency become stricter, innovations in coupling technology continue to emerge. Engineers and manufacturers are now exploring new materials and designs that enhance the performance of pipe couplings. This reflects a broader trend towards sustainability and energy efficiency in engineering, allowing for more reliable systems that reduce waste and conserve resources.
In conclusion, the 3% pipe coupling is a vital element in the effective transport of fluids within many industrial systems. Its design, materials, and installation are all key factors that ensure the reliability and safety of the piping infrastructure. By understanding its importance and adhering to best practices in installation and maintenance, professionals can safeguard their operations against potential failures and contribute to the overall efficiency of their systems. As the industry continues to advance, staying abreast of innovations in pipe coupling technology will be crucial for optimizing fluid transport processes worldwide.
-
Reliable Brake Line Solutions for Your VehicleNewsJun.05,2025
-
Quick Fix for Leaky Air Conditioning HosesNewsJun.05,2025
-
Powerful Sewer Jetting Solutions for Tough ClogsNewsJun.05,2025
-
Power Steering Hose Problems SolvedNewsJun.05,2025
-
Hose Protectors That Actually WorkNewsJun.05,2025
-
Essential Hose Connectors for Every HomeNewsJun.05,2025

